Achilles Tendinitis
Overview
 Achilles tendinitis is one of the more common causes of heel pain and many people describe it as pain in the back of the heel. Since this condition is a form of tendinitis, patients mostly notice that the back of their heel is inflamed. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in your body. It is also one of the most important and most used parts of the body. It is essential for walking, running, jumping or even just an extension of the foot. It is for this reason that Achilles tendinitis can affect anyone who is constantly putting stress on his or her foot. Athletes are particularly at risk.
Achilles tendinitis is one of the more common causes of heel pain and many people describe it as pain in the back of the heel. Since this condition is a form of tendinitis, patients mostly notice that the back of their heel is inflamed. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in your body. It is also one of the most important and most used parts of the body. It is essential for walking, running, jumping or even just an extension of the foot. It is for this reason that Achilles tendinitis can affect anyone who is constantly putting stress on his or her foot. Athletes are particularly at risk.
Causes
The calf is under a lot of strain when running: it is not only put on stretch during landing of the foot, but it also has to produce the tension needed to support body weight and absorb the shock of landing. This is what is called an ?eccentric load?. Excessive eccentric loading - either by way of a dramatic increase in mileage, or excessive hill running, or faulty running posture - could very well be the cause of a runner?s achilles tendinitis. The calf strain translates downward into the achilles tendon where it attaches to the heel, and inflammation ensues. Inflammation then causes scarring and fibrosis of tissues, which in turn inflicts pain upon stretching or use. Risk factors for Achilles tendinitis also include spending prolonged amounts of time standing or walking.
Symptoms
The Achilles tendon is a strong muscle and is not usually damaged by one specific injury. Tendinitis develops from repetitive stress, sudden increase or intensity of exercise activity, tight calf muscles, or a bone spur that rubs against the tendon. Common signs and symptoms of Achilles Tendinitis include, gradual onset of pain at the back of the ankle which may develop in several days up to several months to become bothersome. Heel pain during physical activities which may diminish after warming up in early stages, or become a constant problem if the problem becomes chronic. Stiffness at the back of the ankle in the morning. During inactivity, pain eases. Swelling or thickening of the Achilles tendon. Painful sensation if the Achilles tendon is palpated. If a pop is heard suddenly, then there is an increased chance that the Achilles tendon has been torn and immediate medical attention is needed.
Diagnosis
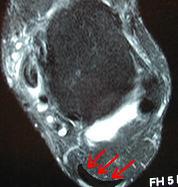
A podiatrist can usually make the diagnosis by clinical history and physical examination alone. Pain with touching or stretching the tendon is typical. There may also be a visible swelling to the tendon. The patient frequently has difficulty plantarflexing (pushing down the ball of the foot and toes, like one would press on a gas pedal), particularly against resistance. In most cases X-rays don't show much, as they tend to show bone more than soft tissues. But X-rays may show associated degeneration of the heel bone that is common with Achilles Tendon problems. For example, heel spurs, calcification within the tendon, avulsion fractures, periostitis (a bruising of the outer covering of the bone) may all be seen on X-ray. In cases where we are uncertain as to the extent of the damage to the tendon, though, an MRI scan may be necessary, which images the soft tissues better than X-rays. When the tendon is simply inflamed and not severely damaged, the problem may or may not be visible on MRI. It depends upon the severity of the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The aim, when treating Achilles tendinitis, is to relieve pain and reduce swelling. The kind of treatment used can vary, based on the severity of the condition and whether or not the patient is a professional athlete. After diagnosis, the doctor will decide which method of treatment is required for the patient to undergo, it is likely that they will suggest a combination. Stretching achilles tendon, a doctor might show the patient some stretching exercises that help the Achilles tendon heal, as well as preventing future injury. Methods used to treat Achilles tendinitis include, ice packs - applying these to the tendon, when in pain or after exercising, can alleviate the pain and inflammation. Resting, this gives the tissue time to heal. The type of rest needed depends on the severity of the symptoms. In mild cases of Achilles tendinitis, it may mean just reducing the intensity of a workout, in severe cases it might mean complete rest for days or weeks. Elevating the foot, swelling can be reduced if the foot is kept raised above the level of the heart. Exercise and stretching, a doctor might show the patient some stretching exercises that help the Achilles tendon heal, as well as preventing future injury. They may, instead, refer the patient to a physiotherapist or another specialist. The exercises learned will improve the flexibility of the area and likely increase calf strength. Pain relievers - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), such as ibuprofen can reduce pain and swelling. If you suffer from asthma, kidney disease or liver disease do not take NSAIDs without first checking with your doctor. Steroid injections, these can reduce tendon swelling, but should be performed with caution, as this process has been associated with a greater risk of tendon rupture. A doctor would likely perform the injection while scanning the area with ultrasound to reduce this risk. Compression bandages and orthotic devices, such as ankle supports and shoe inserts can aid recovery as they take the stress off the Achilles tendon.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered when non-operative measures fail. Patient compliance and postoperative management is an important aspect of the operative management to prevent ankle stiffness or recurrence of the symptoms. Surgery usually requires a removal of the damaged tissue (debridement) and meticulous repair of the tendon. Post-operative immobilization is required, followed by gradual range of motion and strengthening exercises start. It may require 6 months for the full recovery. Some known complication are recurrence, stiffness of the ankle and deep vein thrombosis.
Prevention
Suggestions to reduce your risk of Achilles tendonitis include, icorporate stretching into your warm-up and cool-down routines. Maintaining an adequate level of fitness for your sport. Avoid dramatic increases in sports training. If you experience pain in your Achilles tendon, rest the area. Trying to ?work through? the pain will only make your injury worse. Wear good quality supportive shoes appropriate to your sport. If there is foot deformity or flattening, obtain orthoses. Avoid wearing high heels on a regular basis. Maintaining your foot in a ?tiptoe? position shortens your calf muscles and reduces the flexibility of your Achilles tendon. An inflexible Achilles tendon is more susceptible to injury. Maintain a normal healthy weight.
 Achilles tendinitis is one of the more common causes of heel pain and many people describe it as pain in the back of the heel. Since this condition is a form of tendinitis, patients mostly notice that the back of their heel is inflamed. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in your body. It is also one of the most important and most used parts of the body. It is essential for walking, running, jumping or even just an extension of the foot. It is for this reason that Achilles tendinitis can affect anyone who is constantly putting stress on his or her foot. Athletes are particularly at risk.
Achilles tendinitis is one of the more common causes of heel pain and many people describe it as pain in the back of the heel. Since this condition is a form of tendinitis, patients mostly notice that the back of their heel is inflamed. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in your body. It is also one of the most important and most used parts of the body. It is essential for walking, running, jumping or even just an extension of the foot. It is for this reason that Achilles tendinitis can affect anyone who is constantly putting stress on his or her foot. Athletes are particularly at risk.
Causes
The calf is under a lot of strain when running: it is not only put on stretch during landing of the foot, but it also has to produce the tension needed to support body weight and absorb the shock of landing. This is what is called an ?eccentric load?. Excessive eccentric loading - either by way of a dramatic increase in mileage, or excessive hill running, or faulty running posture - could very well be the cause of a runner?s achilles tendinitis. The calf strain translates downward into the achilles tendon where it attaches to the heel, and inflammation ensues. Inflammation then causes scarring and fibrosis of tissues, which in turn inflicts pain upon stretching or use. Risk factors for Achilles tendinitis also include spending prolonged amounts of time standing or walking.
Symptoms
The Achilles tendon is a strong muscle and is not usually damaged by one specific injury. Tendinitis develops from repetitive stress, sudden increase or intensity of exercise activity, tight calf muscles, or a bone spur that rubs against the tendon. Common signs and symptoms of Achilles Tendinitis include, gradual onset of pain at the back of the ankle which may develop in several days up to several months to become bothersome. Heel pain during physical activities which may diminish after warming up in early stages, or become a constant problem if the problem becomes chronic. Stiffness at the back of the ankle in the morning. During inactivity, pain eases. Swelling or thickening of the Achilles tendon. Painful sensation if the Achilles tendon is palpated. If a pop is heard suddenly, then there is an increased chance that the Achilles tendon has been torn and immediate medical attention is needed.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist can usually make the diagnosis by clinical history and physical examination alone. Pain with touching or stretching the tendon is typical. There may also be a visible swelling to the tendon. The patient frequently has difficulty plantarflexing (pushing down the ball of the foot and toes, like one would press on a gas pedal), particularly against resistance. In most cases X-rays don't show much, as they tend to show bone more than soft tissues. But X-rays may show associated degeneration of the heel bone that is common with Achilles Tendon problems. For example, heel spurs, calcification within the tendon, avulsion fractures, periostitis (a bruising of the outer covering of the bone) may all be seen on X-ray. In cases where we are uncertain as to the extent of the damage to the tendon, though, an MRI scan may be necessary, which images the soft tissues better than X-rays. When the tendon is simply inflamed and not severely damaged, the problem may or may not be visible on MRI. It depends upon the severity of the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The aim, when treating Achilles tendinitis, is to relieve pain and reduce swelling. The kind of treatment used can vary, based on the severity of the condition and whether or not the patient is a professional athlete. After diagnosis, the doctor will decide which method of treatment is required for the patient to undergo, it is likely that they will suggest a combination. Stretching achilles tendon, a doctor might show the patient some stretching exercises that help the Achilles tendon heal, as well as preventing future injury. Methods used to treat Achilles tendinitis include, ice packs - applying these to the tendon, when in pain or after exercising, can alleviate the pain and inflammation. Resting, this gives the tissue time to heal. The type of rest needed depends on the severity of the symptoms. In mild cases of Achilles tendinitis, it may mean just reducing the intensity of a workout, in severe cases it might mean complete rest for days or weeks. Elevating the foot, swelling can be reduced if the foot is kept raised above the level of the heart. Exercise and stretching, a doctor might show the patient some stretching exercises that help the Achilles tendon heal, as well as preventing future injury. They may, instead, refer the patient to a physiotherapist or another specialist. The exercises learned will improve the flexibility of the area and likely increase calf strength. Pain relievers - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), such as ibuprofen can reduce pain and swelling. If you suffer from asthma, kidney disease or liver disease do not take NSAIDs without first checking with your doctor. Steroid injections, these can reduce tendon swelling, but should be performed with caution, as this process has been associated with a greater risk of tendon rupture. A doctor would likely perform the injection while scanning the area with ultrasound to reduce this risk. Compression bandages and orthotic devices, such as ankle supports and shoe inserts can aid recovery as they take the stress off the Achilles tendon.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered when non-operative measures fail. Patient compliance and postoperative management is an important aspect of the operative management to prevent ankle stiffness or recurrence of the symptoms. Surgery usually requires a removal of the damaged tissue (debridement) and meticulous repair of the tendon. Post-operative immobilization is required, followed by gradual range of motion and strengthening exercises start. It may require 6 months for the full recovery. Some known complication are recurrence, stiffness of the ankle and deep vein thrombosis.
Prevention
Suggestions to reduce your risk of Achilles tendonitis include, icorporate stretching into your warm-up and cool-down routines. Maintaining an adequate level of fitness for your sport. Avoid dramatic increases in sports training. If you experience pain in your Achilles tendon, rest the area. Trying to ?work through? the pain will only make your injury worse. Wear good quality supportive shoes appropriate to your sport. If there is foot deformity or flattening, obtain orthoses. Avoid wearing high heels on a regular basis. Maintaining your foot in a ?tiptoe? position shortens your calf muscles and reduces the flexibility of your Achilles tendon. An inflexible Achilles tendon is more susceptible to injury. Maintain a normal healthy weight.
